Piperine can regulate the permeability of the intestinal lining, which determines what substances pass from the digestive tract into the bloodstream.
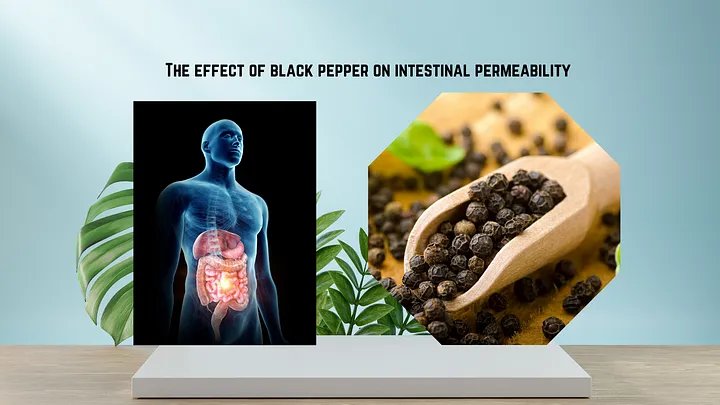
The effect of piperine on intestinal permeability is particularly important in the context of nutritional supplements and medications. This significantly improves the therapeutic effectiveness of compounds that are otherwise metabolized and excreted rapidly.
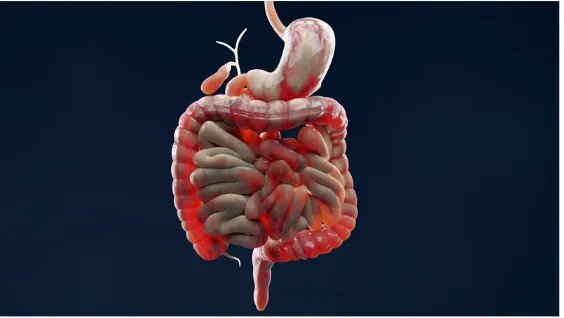
One of the most well-studied interactions is between piperine and curcumin, the active compound in turmeric.
When curcumin is combined with piperine, the bioavailability of curcumin increases by 2000%.
Curcumin is known for its potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties but has poor bioavailability because it is rapidly metabolized.

Black pepper is made from the unripe berries of the Piper nigrum plant. The berries are picked when still green, cooked briefly, and dried until they shrivel and turn black.

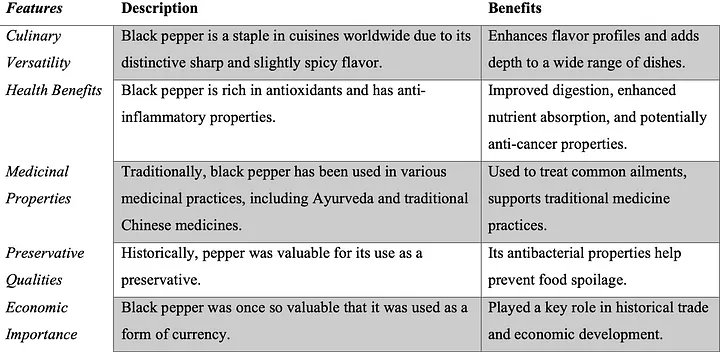
Black pepper is incredibly versatile and can be used in a wide range of culinary applications to enhance flavor, add spice, and even provide subtle complexity to dishes:

Some studies have explored the potential of black pepper, specifically its active compound piperine, to aid in weight loss.
These mechanisms suggest that piperine from black pepper could be a beneficial addition to a diet aimed at weight loss.
However, these effects must be better understood through more comprehensive human studies to fully assess the efficacy and safety of black pepper or piperine supplements for weight loss.
Both come from the Piper nigrum plant. Black pepper is made from unripe berries, while white pepper comes from fully ripened berries with removed outer skin.
Black pepper retains its flavor best when stored in a cool, dark place, preferably in an airtight container to keep it fresh longer.
Freshly ground black pepper is often more flavorful than pre-ground pepper because it retains more natural oils and aroma.
While black pepper is commonly used and safe for most people in culinary amounts, excessive consumption can lead to some side effects, particularly for those with certain health conditions or sensitivities.
Using black pepper in moderation within dietary limits is generally recommended to avoid these potential side effects.
Individuals with specific health conditions or those on medication should consult healthcare providers to ensure safe consumption levels.
Black pepper, often referred to as “black gold,” was historically one of the most traded spices in the world, mainly due to its importance as a culinary and medicinal ingredient.
The spice’s ability to enhance the absorption of nutrients, like the increase in curcumin’s bioavailability when combined with piperine (up to 2000%), has made it a critical ingredient in both ancient and modern diets.
Disclosure: None of the content above should be considered medical advice. We recommend always consulting a medical professional for medical advice.